
Artificial intelligence and Large Language Models are buzzwords heard in nearly every industry. Many companies are wondering how to use them safely and which solution will be the most effective. There are plenty of options—and they’re often hard to tell apart. In this article, we break them down in a clear and easy-to-understand way.
AI can take on many roles in a company—as a chatbot, assistant, agent, data analysis tool, content generator, or knowledge search engine. So how can you choose the solution that best fits your employees’ needs? It helps to understand what each option has to offer.
Chatbot – answers questions, provides explanations, and handles requests
This is the most common use of AI in areas such as customer service and sales. An AI chatbot based on a large language model, such as ChatGPT, can hold natural conversations, understand the context of inquiries, and deliver accurate answers—24/7, in multiple languages, and without human involvement.
These solutions are typically implemented on websites, in messaging platforms (like Messenger or WhatsApp), or within helpdesk systems, where they assist with answering questions, tracking orders, or providing product information. As a result, they significantly automate customer service, reduce operational costs, and improve customer satisfaction ratings.
For the purposes of this article, we define a chatbot as an AI interface primarily intended for external users—in other words, it operates “outside the company.” This definition distinguishes it from AI agents, which perform more complex tasks within internal processes by integrating with systems, databases, or APIs.
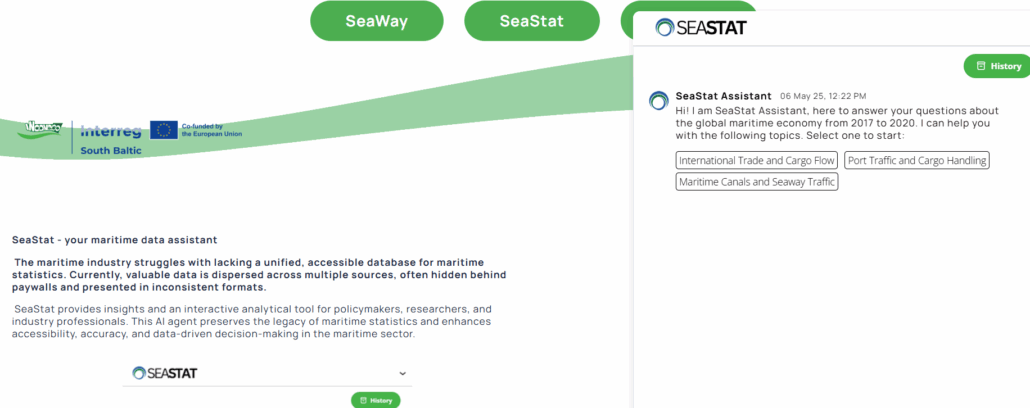
AI Agent – a tool designed to carry out specific tasks
Unlike a chatbot, which interacts with external users, an AI agent operates within the organization and supports employees by automating specific business processes. It’s not a one-size-fits-all tool—it’s built with a clearly defined purpose in mind, such as document processing, data analysis, or integration with ERP systems.
Thanks to large language models like Gemini or Claude, an AI agent can understand context, make decisions, and trigger specific actions—without human input. It can run in the background, process data from multiple sources, manage files, or handle email inboxes. Each AI agent is tailored to the company’s individual needs and specific tasks. Only then can it offer real value instead of becoming just another generic tool.
Want to see how this works in practice?
Check out our case study: Meet your personal AI agent-a case study for a freight forwarding company – where we describe how we built an agent integrated with an email inbox.
AI Assistant – supports users in daily work by operating contextually and “in the background”
Unlike a chatbot that answers questions or an agent that automates a specific process, an AI assistant is a tool that works alongside employees in real time—it understands context, suggests next steps, and makes tasks easier within familiar applications.
It’s typically integrated into a specific work environment, such as a word processor, spreadsheet, CRM, or project management tool. The assistant doesn’t replace the user—it actively supports them in making decisions, writing, analyzing data, or planning.
AI assistants like GitHub Copilot, Notion AI, or Google’s Workspace assistant show how this technology can genuinely boost team productivity and reduce time spent on routine tasks. From a business perspective, a well-designed assistant can improve work quality, reduce errors, and make onboarding new employees easier.
Other Business Applications of Large Language Models
The possibilities go far beyond chatbots, assistants, or agents. These models can take on specialized roles, supporting tasks such as document processing, data analysis, or content creation. They’re increasingly used to automatically summarize reports, extract information from unstructured sources (like emails, PDFs, or scanned forms), or answer natural-language questions based on internal documentation.
LLMs can also assist marketing teams by generating suggestions for ad copy, product descriptions, or sales messages tailored to the company’s style. In analytics departments, they provide faster access to data—generating database queries, interpreting results, and presenting insights in a way that’s easy for non-technical users to understand. These applications often don’t require building a new tool from scratch, but rather integrating the AI model into existing company systems. This way, the technology supports specific tasks—right where it’s needed.
AI Models and Data Security
Business owners and managers still approach AI tools with caution, mainly because they’re unsure how to ensure the security and confidentiality of processed data. We’ve explored these topics in previous publications that are worth reviewing.
In the article “AI User Privacy: An Analysis of Platform Policies”, we outlined the data privacy and model training policies followed by major AI providers such as OpenAI, Google Gemini, Microsoft’s Azure OpenAI, and Anthropic’s Claude.
For those considering an on-premise solution, we recommend the blog post “Top Lightweight LLMs for Local Deployment” There, we reviewed several top open-source lightweight LLMs and explained how to run them on a local Windows machine—even with limited GPU resources.
Choosing the right AI tool for your company depends primarily on the goal it’s meant to achieve. A chatbot works best where quick and accessible customer service is key. An AI agent can automate repetitive internal processes and improve information flow between systems. An AI assistant provides day-to-day support for employees—offering suggestions, summaries, or preparing data for further use.
Large language models also allow integration with existing processes—without the need to build a dedicated tool from scratch. However, implementing AI-based technology requires a well-thought-out decision, taking into account both efficiency and data security. If you’re looking to adopt AI in your company and need an experienced partner to guide you through the process, get in touch with us.

